Osteocartilage degeneration is a degenerative nutritional disease in the cartilage tissue of the vertebrae, causing its deformation and destruction.Osteocartilage can develop in one or more spines.Osteochondral disease in the cervical areaIt occurs especially frequently and sometimes produces very serious complications.

Characteristics of osteomyelitis of cervical vertebrae
Due to the characteristics of the cervical vertebrae structure, the process and symptoms of osteochondrosis in this segment have many characteristics.The cervical spine is composed of small movable vertebrae that often bear large and long loads.The spinal canal in the cervical vertebra is the narrowest, so the compression of the spinal cord in this segment develops more frequently and leads to quite severe lesions.In the neck, there is a large accumulation of nerve ends and blood vessels, including vertebral arteries, which provide nutrition for the cerebellum, oblong brain and back of the brain.This artery violation of blood flow can lead to a violation of coordination, dizziness, loss of vision and hearing, and in severe cases, stroke may occur.
Symptoms of cervical vertebrae
Osteochondral disease in the cervical areaThe spine is manifested by several syndromes:
-
Reflex syndrome
Areas of pain and accumulation of cervical spine, appearing after a sneeze, sudden movement of the head or long static states, such as sleep or fixed states, and subsequent movement of the head or neck or neck - often complain about the osteocartilage of the cervical spine.The pain can radiate to the shoulder or chest cage. Spine canal stenosis syndrome (spine stenosis)
The syndrome is formed by compression (squeezing) of the spinal cord and its blood vessels, which leads to circulatory diseases and the development of bone marrow disease in the affected area - the rare but most powerful complication of osteochondrosis.vertro-Carbon neck marrow disease mainly occurs in the middle and elderly people, which is due to spinal cord compression or its blood vessels with posterior base lobes, thickening of yellow ligaments, and hernia of vertebral discs.First, it is often observed that the disease gradually develops pain and limitations of cervical spine movement.In the future, cervical osteochondrosis can lead to impaired function of the upper and/or lower limbs, manifested as numbness, tingling sensation on the fingers, a feeling of cotton legs or arms-
Rook syndrome
The manifestation of radiation syndrome in cervical osteocartilage will depend on which nerve root compression occurs due to structural changes in the disc.However, in any case, cervical osteocartilage can occur, and headaches are characterized by soreness, pulsation, or burning, sometimes flowing in the type of hypertension.Back pain is rarely local and usually gives shoulder blades, forearms, shoulders and/or hands, until the fingers of the brush.
Depending on the affected spinal segment, the following symptoms may be:
- C1-C2: Usually, this part of the failure occurs due to car injuries and manifests as odor and speech violations, atrophy of facial and sublingual muscles, and reduced sensitivity in the occipital area.
- C2-C3: It is also rarely affected and is accompanied by impaired movement and sensitivity of hearing, vision and control of speech muscles, which can lead to speech disorders and taste sensations, inflammation, sweating or throat lumps.
- C3-C4: In addition to pain in the clavicle and shoulder GPU, the diaphragmagmmantagic nerves retire in this section, spam and trapezoidal muscles of the belt, pain in the lower right cartilage and heart also develops, and respiratory movements are also disturbed.In addition, great elasticity, nasal congestion, swelling, reduced odor, sagging face, and worsening teeth condition may develop.
- C4-C5: Failure in this section is accompanied by pain in the shoulders, atrophy of the deltoid muscles, reduced sensitivity to the outer surface of the shoulder, comfort of the shoulders, inflammation of the shoulders and inflammation of the skeletal muscles in this area.Among other symptoms, the sound may change, the feeling of inflammation in the throat, and the call is Nor.
- C5-C6: This segment is often susceptible to degenerative disease lesions and has a wide range of symptoms.First, pain and impaired skin sensitivity from the shoulder blade, outer surface of the shoulder to the radial surface of the forearm and thumb of the hand.Subsequently, somatic symptoms appear, including frequent treatment of the lungs and bronchials, including asthma, rheumatism and allergic manifestations, which are symptoms of angina.
- C6-C7: Lesions in this part of the nerve roof cause pain in the shoulder cap bone, the posterior surface of the shoulder, along the pre-examination surface of the forearm to the back of the hand.In addition, damage to this segment may be accompanied by symptoms corresponding to thyroid disease, mediastinal organs and cardiovascular system.
- C7-T1: C8 The lesions of the spine are accompanied by hypertrophy of the triceps, which transfer the small fingers, which can lead to weakening of flexion reflexes and pain, impaired skin sensitivity, neck, shoulders, shoulders, shoulder blades, elbows and small fingers.In severe cases, symptoms may develop the same as angina, arrhythmia, and asthma.
-
Heart syndrome of cervical osteochondrosis
Cardiac syndrome develops due to diaphragmm (diaphragmantic nerve) or nerve roots innervated by the muscles of the large chest.These symptoms are definitely the same as the attack of angina, but at the same time, the attack does not last long, and the pain increases with a sharp movement of the head or neck, with a sharp sneezing or coughing.Standard coronary arteries do not bring relief relief, and the electrocardiogram showed no behavior that invaded the coronary circulation at the time of the attack.At the same time, cardiac syndrome can be accompanied by tachycardia, arrhythmia and hypertension. -
Driven arterial syndrome
This syndrome is one of the most common and dangerous symptomsOsteochondral disease in the cervical areaspine.This syndrome develops in the context of vertebral artery and circulatory diseases that squeeze corresponding areas of the brain (cerebellum, brainstem and posterior lobe), which determines the clinical status.
One of the main manifestations of vertebral artery syndrome is a strong pulsation and/or burning headache, constant or paroxysmal, exciting darkness, spanning parts, whiskey and behind.Often, pain can be one aspect.In the first stage of development, headaches can occur or exacerbate when staying in an uncomfortable position for a long time, physical fatigue or sudden exercise.As the lumen narrows, the painful arteries become more pronounced, frequent, and sometimes persist.In severe cases or at the peak of headache, vomiting may occur and fainting cannot be ruled out.
Visual diseases with cervical bone-cartilage degeneration can occur separately or in the context of headaches and are expressed by pain in the eyeball, impaired vision, veil feeling in front of the eyes, dry eyes or stove.One of the characteristics of narrowing vertebral artery is a sudden short-term episode of dizziness or loss of direction in space.This attack took place for a few seconds and passed quickly.Sudden noise in the ears or pulsations in the head area may occur.Similarly, damage to the vertebral artery may lead to the development of cardiac syndrome.
In severe cases, attacks are damaged by severe headache, vomiting, loss of movement coordination, handwriting changes, gait shaking, double attitude, speech and balance.
Diagnosis of osteochondral disease in the cervical spine
Doctors can make a primary diagnosis of osteochondrosis in the cervical spine by the first examination of the patient and determine the level, anatomical characteristics of the affected spine, including posture, physique, body structure, spicy process line, spicy process, lateral profile of the neck, the lower corner of the shoulder blades bone; the positioning, nature and extent of the pain syndrome; the amplitude, relief, and muscle tone of the spine.
The diagnosis is specified using a visual diagnostic method (radiology research, CT, MRI), which allows you to determine the stage of the disease, the level of spinal lesions, and the accurate positioning of the deformed disc.Based on these data, the best treatment for cervical osteochondrosis was selected.
Treatment of cervical vertebrae bone marrow disease
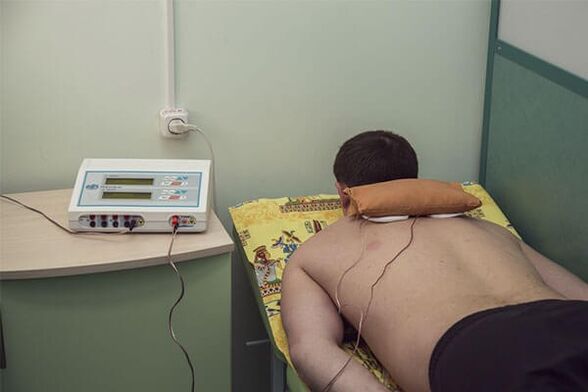
In the treatment of cervical osteocartilage, surgical and conservative methods are used.However, surgical treatment is only prescribed in the presence of serious complications that occur later in the osteochondrosis:
- The stenosis (stenosis) that forms the spinal canal;
- The vertebral artery is inhibited;
- An important hernia or protrusion is formed, compressing the nerve roots.
- Excessive instability of the spine.
In other cases, treatment standardsOsteochondral disease in the cervical areaThe spine is a conservative therapy.This is due to the fact that with all the achievements of modern medicine, the consequences of surgical intervention are not always expected.
Conservative treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
The best results in treatmentOsteochondral disease in the cervical areaWhen you go to a doctor, the spine and other types of osteochondrosis can be achieved.Unfortunately, many patients usually don’t have mild discomfort with back or periodic headaches.On the other hand, there are many cases of improper diagnosis and long-term useless treatment, becauseOsteochondral disease in the cervical areaThe spine can simulate other diseases such as arthritis, myalgia, or angina.This is why vertebral encephalologists recommend checking the spine when there are symptoms of any disease, especially with head or spine pain.
In the effective treatment of cervical osteocartilage, comprehensive methods are very important, including the following directions:
- Drug Therapy- Designed to improve malnutrition in the intervertebral disc and stop pain, eliminating muscle cramps and inflammation during aggravation.For these purposes, to stimulate the recovery of cartilage tissue in the joint, the recovery of multivitamins and vitamins in Group B;
- physiotherapy- The prescription is to relieve pain, improve the nutrition of intervertebral disc cartilage tissue, stimulate the process of cartilage regeneration, remove muscle spasms, and postoperative inflammation to recover quickly;
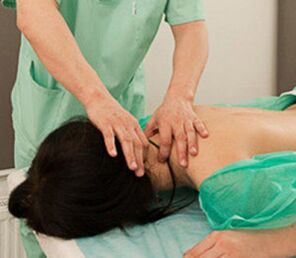
- Manual therapy- It is used to eliminate muscle cramps, reduce pain, improve blood and lymph metabolism, correct posture and improve joint amplitude.Select a manual exposure regimen for each patient;
- massage- Long-term and mature methods for treating diseases of the musculoskeletal system.Have the same effect as manual therapy;
- Medical SportsIt is one of the most important methods for treating all types of osteochondrosis, including osteochondrosis in the cervical spine.The purpose of exercise therapy is to reduce muscle spasms and compression of nerve roots, improve blood and lymph flow to the spine, enhance muscle frames and improve the flexibility of the ligament instrument.For each patient, a set of exercises was selected, correctly implemented by experts monitoring;
- ReflectionReferring to an alternative type of treatment, widely used today and combined with other treatments, gives good results.The essence of this method is the effect on the acupuncture point and/or the reflex-generating area to achieve the same results as other treatments (reducing muscle pain and cramps, decompression at the spinal cord and brain root, improving tissue nutrients in vertebral tissue), and improving sleep, improving sleep, mental weight effects, and radiating weight effects, and radiating ranges for weight gain to enhance ranges.
To treat chronic osteochondrosis, cartilage protectors, vitamins (B6, B12) in Group B and drugs for external uses - ointments, creams, gels containing NSAIDs, local annoyances and tissue regeneration stimulators were also used.
In addition to the primary treatment, patients are advised to use cervical osteocartilage degeneration to change their usual lifestyle because in most cases, the disease is performed under low mobility, poverty or malnutrition, obesity, obesity or excessively low communication and poor intimacy.In most cases, in the early stages of cervical osteochondria, it is sufficient to achieve a healthy lifestyle, not allowing muscle cramps and muscle overload in the cervical scintillation area, providing comfortable conditions for sleep, providing normal nutrition for nutrition and implementing doctor's advice to prevent doctor's advice from further development, and first recovering that phase and accidentally resumed the campaign.